
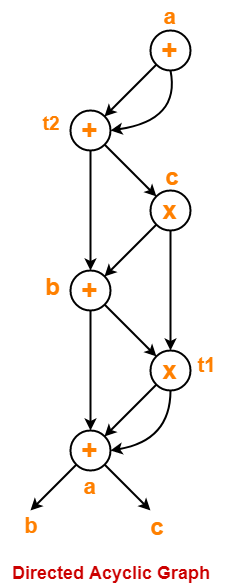
This representation is an enhancement over triples representation. Triples face the problem of code immovability while optimization, as the results are positional and changing the order or position of an expression may cause problems. They are equivalent to DAG while representing expressions. Represent similarity with DAG and syntax tree. The above example is represented below in quadruples format: OpĮach instruction in triples presentation has three fields : op, arg1, and arg2.The results of respective sub-expressions are denoted by the position of expression. QuadruplesĮach instruction in quadruples presentation is divided into four fields: operator, arg1, arg2, and result. A three-address code can be represented in two forms : quadruples and triples. R being used as registers in the target program.Ī three-address code has at most three address locations to calculate the expression. The intermediate code generator will try to divide this expression into sub-expressions and then generate the corresponding code. Therefore, code generator assumes to have unlimited number of memory storage (register) to generate code. Intermediate code tends to be machine independent code. That syntax tree then can be converted into a linear representation, e.g., postfix notation. Intermediate code generator receives input from its predecessor phase, semantic analyzer, in the form of an annotated syntax tree. Intermediate code can be either language specific (e.g., Byte Code for Java) or language independent (three-address code). It is good for machine-dependent optimizations.

Low Level IR - This one is close to the target machine, which makes it suitable for register and memory allocation, instruction set selection, etc. But for target machine optimization, it is less preferred. They can be easily generated from the source code and we can easily apply code modifications to enhance performance.

High Level IR - High-level intermediate code representation is very close to the source language itself. Intermediate codes can be represented in a variety of ways and they have their own benefits. It becomes easier to apply the source code modifications to improve code performance by applying code optimization techniques on the intermediate code. The second part of compiler, synthesis, is changed according to the target machine. Intermediate code eliminates the need of a new full compiler for every unique machine by keeping the analysis portion same for all the compilers. If a compiler translates the source language to its target machine language without having the option for generating intermediate code, then for each new machine, a full native compiler is required. A source code can directly be translated into its target machine code, then why at all we need to translate the source code into an intermediate code which is then translated to its target code? Let us see the reasons why we need an intermediate code.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
